What Are Google Ads? A Beginner’s Guide to Navigating Google’s Advertising Platform
what are Google Ads
Google Ads is a cornerstone in digital marketing, offering businesses a platform to reach potential customers through targeted advertising. This platform spans Google’s vast network, including search results, YouTube, Google Shopping, and various apps, enabling advertisers to connect with their audience in a highly contextual and engaging manner.

Benefits of Using Google Ads:
Broad Reach: Google’s vast network allows ads to reach many internet users, including mobile devices and tablets.
Targeted Advertising: The platform’s targeting capabilities ensure that ads are shown to the audience most likely to be interested in the products or services offered.
Cost Control: Advertisers can set daily budgets and maximum campaign bid amounts, providing control over advertising spend.
Immediate Visibility: Unlike organic search marketing efforts that can take time to build visibility, Google Ads can provide immediate online visibility.
Measurable ROI: Every aspect of a Google Ads campaign is measurable, from the number of impressions and clicks to conversions and ROI, allowing for data-driven decision-making.
Google Ads is a powerful tool for businesses of all sizes looking to increase their online presence, drive traffic to their website, and, ultimately, generate sales or leads.
HOW ARE GOOGLE ADS WORK?
Google Ads allows advertisers to place bids on the opportunity to display their ads to users across Google’s vast network, including search results, websites, videos, and mobile apps. This system is primarily based on a pay-per-click (PPC) model, where advertisers pay a fee each time a user clicks on one of their ads. Here’s a breakdown of how Google Ads operates:
- Keyword Selection
Advertisers select keywords relevant to their business, products, or services. These keywords are the terms that users might enter into a search engine when looking for similar offerings. Advertisers bid on these keywords, competing with others who want to target the same terms. - Ad Creation
Advertisers create ads that will be shown to users. These ads can come in various formats, including text ads that appear on search results pages, display ads that include images or videos and appear on websites within the Google Display Network, and shopping ads that show products and prices. - Bidding and Auction
Each time a Google search is performed, or a site on the Google Display Network is visited, Google runs an auction to determine which ads will be shown. Advertisers set bids, the maximum amount they’re willing to pay for a click on their ad. However, the actual amount paid can be less, determined by the auction. - Quality Score and Ad Rank
Google doesn’t decide on placement based solely on the highest bidder. It also considers the relevance and quality of the ads and the landing pages they link to. This is measured by the Quality Score, which factors in click-through rate (CTR), ad relevance, and landing page experience. Google combines the bid amount and Quality Score to determine the Ad Rank, which decides the placement of ads. - Targeting Options
Beyond keywords, advertisers can refine their audience through various targeting options, including:
Demographics: Age, gender, income level, etc.
Location: Targeting by country, region, city, or even a specific radius around an area.
Device: Targeting specific devices like desktops, tablets, or mobile phones.
Time: Choosing specific days of the week or times of day for ads to appear.
Audience behavior: Including interests, past website visits, and more. - Pay-Per-Click (PPC)
Advertisers only pay when a user clicks on their ad. This model allows for tight budget control and measurement of ROI. Advertisers can set daily budgets to limit their total spend. - Performance Measurement and Optimization
Google Ads provides detailed analytics and performance metrics, such as impressions (how often the ad is shown), clicks, conversion rates, and more. Advertisers use this data to assess their campaign’s effectiveness and make adjustments to improve performance. This can include changing bid amounts, refining targeting, tweaking ad copy, and optimizing landing pages.
Google Ads campaign:
In Google Ads, the structure of any advertising effort can be broken down into three primary levels: Campaign, Ad Group, and Ad Level. Understanding each level is crucial for effective ad management and optimization. Here’s an overview of each level within the context of a Google Ads campaign - Campaign Level
The campaign level is the highest and most general level of organization within Google Ads. Advertisers define their advertising efforts’ overarching goals and parameters at this level. Key settings and decisions made at the campaign level include:
WHAT ARE GOOGLE ADS
In Google Ads, the structure of your advertising efforts is organized into three primary levels: Campaign, Ad Group, and Ad Level. Each level serves a different purpose and allows various types of customization and specificity in targeting and messaging. Understanding these levels and the types of ads you can create within them is crucial for effective campaign management.
what are Campaign Levels
At the campaign level, you’re setting the broadest parameters of your ad efforts, including the objective, budget, and overall strategy. Here are the main types of campaigns you can create:
Search Campaigns: Ads appear on Google Search results pages and other Google sites when someone searches for terms related to one of your keywords.
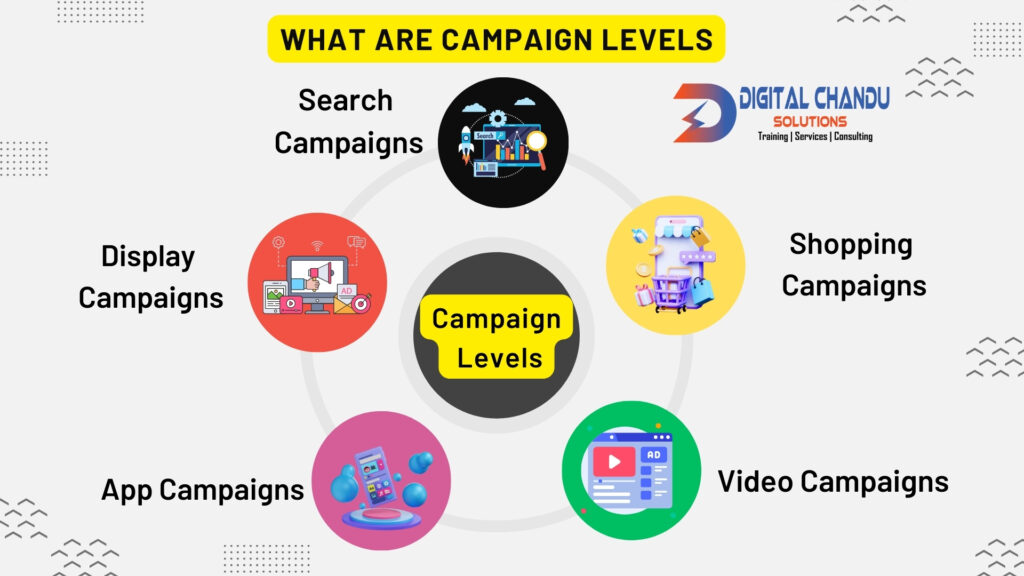
Display Campaigns: Ads are shown across the Google Display Network, which includes millions of websites, news pages, blogs, and Google sites like Gmail and YouTube.
Shopping Campaigns: Product listings appear in Google Shopping and Google Search when someone searches for products you sell.
Video Campaigns: Ads are played before or during YouTube videos or on partner sites and apps in the Display Network.
App Campaigns: Promote your mobile app across Google’s Search Network, Play Store, YouTube, and the Google Display Network.
Ad Group Level
Within each campaign, ad groups help organize your ads by a common theme. For example, in a Search Campaign, ad groups might be collected by different product types or services. Types of ad group organization depend on the campaign type but generally revolve around specific targeting or thematic cohesion.
what are Ad Level
At the ad level, you’re creating content that users will see. The types of ads you can create vary by the campaign type:
Text Ads: Primarily for Search and Display campaigns, consisting of headlines, descriptions, and a display URL.
Responsive Search Ads: These are available in search campaigns, where you provide multiple headlines and descriptions, and Google automatically tests different combinations to learn which performs best.
Image Ads: Used in Display campaigns, these can be static or animated images designed to grab attention and encourage clicks.
Video Ads: For Video campaigns, these ads appear on YouTube and across Google’s video partners. Formats include skippable and non-skippable in-stream ads, video discovery ads, and bumper ads.
Product Shopping Ads: Specific to Shopping campaigns, these ads show users a photo of your product, a title, price, store name, and more.
App Ads: In in-app campaigns, you provide text, images, or videos, and Google automatically designs a variety of ads to be displayed across its networks.
Showcase Shopping Ads: Also part of Shopping campaigns, these ads allow you to group a related set of products and present them to introduce your brand or business.
what is Ad Rank
Ad Rank determines the position of your ads on Google’s Search Engine Results Page (SERP). It’s not just the highest bidder who gets the top spot, but the advertiser with the highest Ad Rank. This ensures that users are always shown ads most relevant to their queries, providing a better search experience. The components of Ad Rank include:
Bid Amount: How much will you pay per click on your ad?
Quality Score: A metric that evaluates the quality and relevance of your ads and keywords.
Ad Relevance: How closely your ad matches the intent behind a user’s search.
Landing Page Experience: The relevance and usability of the landing page to which your ad directs users.
Expected Click-Through Rate (CTR): The likelihood of your ad being clicked when shown.
Ad Formats and Extensions: The impact of additional information in your ad, such as phone numbers, site links, or other extensions.
Google calculates Ad Rank every time your ad is eligible to appear for a search query, so your ad’s position can vary depending on the competition and the context of each search.
What is Quality Score
Quality Score is a diagnostic tool that shows how well your ad quality compares to other advertisers. This score is reported on a scale from 1 to 10 and includes the following components:
Expected Click-Through Rate (CTR): An estimate of how often your ad will be clicked when shown for a keyword based on your ad’s historical clicks and impressions.
Ad Relevance: How closely your ad matches the intent behind a user’s search, assessed by analyzing the language in your ad.
Landing Page Experience: How relevant and useful your landing page is to people who click your ad, which includes the page’s content, navigability, and transparency.
Quality Score reflects the overall health of your campaigns and influences your Ad Rank and the cost-per-click (CPC) of your ads. A higher Quality Score means your ad and website are deemed more relevant and valuable to someone looking at your ad, which can lead to lower costs and better ad positions.
Why They Matter
Higher Visibility at Lower Costs: Ads with higher Quality Scores and better Ad Ranks can appear higher on the SERP at lower costs. This is because Google rewards relevant, high-quality ads with better positions and lower CPCs.
Better Budget Efficiency: By optimizing for Quality Score, you can use your advertising budget more efficiently. High-quality ads can lead to reduced costs and more conversions.
Improved Ad Performance: Higher Ad Ranks increase the likelihood that users will see and click your ads, leading to higher conversion rates and more effective campaigns.
Improving your Quality Score and Ad Rank requires regular monitoring and optimization of your campaigns, focusing on creating relevant ads, selecting appropriate keywords, and providing a good user experience on your landing pages.
What are Bidding Strategies
In Google Ads, bidding types refer to the strategies advertisers use to manage how they pay for user interactions with their ads, such as clicks, impressions, or conversions. These strategies align with the advertiser’s goals, such as driving traffic, increasing visibility, or generating conversions. Here’s an overview of the primary bidding types available in Google Ads:
- Cost-per-click (CPC) Bidding
Manual CPC Bidding allows you to set your maximum cost-per-click for your ads. This control can help manage your budget and is helpful for campaigns where you know the value of a click.
Enhanced CPC (ECPC) adjusts your manual bids up or down based on each click’s likelihood of a sale or conversion, helping you get more value from your ad spend. - Cost-Per-Thousand Impressions (CPM) Bidding
CPM Bidding is available for Display Network and YouTube campaigns. You pay based on the number of impressions (views) your ads receive, not clicks. This strategy is ideal for increasing brand awareness. - Cost-Per-View (CPV) Bidding
CPV Bidding is used for Video campaigns. You pay for video views or interactions, such as clicks on call-to-action overlays (CTAs), cards, and companion banners. A view is counted when someone watches 30 seconds of your video (or the duration if it’s shorter than 30 seconds) or interacts with the video, whichever comes first.

- Cost-Per-Acquisition (CPA) Bidding
Target CPA Bidding lets you set a target cost-per-acquisition, and Google Ads automatically sets your bids to help get as many conversions as possible at the target CPA you set. This is ideal for advertisers focused on conversion optimization. - Return on Ad Spend (ROAS) Bidding
Target ROAS Bidding sets bids to achieve an average return on ad spend. You put a target ROAS percentage, and Google Ads will automatically adjust your bids to try and reach that target across all campaigns using this strategy. - Maximize Clicks
An automated bid strategy that sets your bids to help get as many clicks as possible within your budget. This is a simple way to increase website visits. - Maximize Conversions
An automated strategy that automatically sets bids to help get the most conversions for your campaign while spending your budget. - Maximize Conversion Value
This bidding strategy aims to maximize the total conversion value of your campaign within your specified budget, focusing on driving the most valuable conversions. - Percentage of Impressions (vCPM) Bidding
vCPM Bidding (viewable CPM) lets you bid for impressions when your ad is visible on screen. This is available for Display Network campaigns and is suitable for advertisers who prioritize ad viewability.
What are the rules in Google Ads?
Google Ads has a comprehensive set of rules and policies to ensure a safe, fair, and positive experience for users, advertisers, and publishers. These rules govern ad content, practices, and technical implementation. Violating these policies can result in rejected ads, paused campaigns, or even account suspension. Below are some key categories of Google Ads rules:
- Prohibited Content
Illegal Products or Services: Ads must not promote products, services, or illicit activities in the targeted location.
Dangerous Products or Services: Selling or promoting weapons, explosives, tobacco products, and other harmful substances is prohibited.
Inappropriate or Offensive Content: Ads must not contain content that promotes hatred, intolerance, discrimination, or violence. - Prohibited Practices
Misrepresentation: Advertisers must accurately represent their products, services, and websites, avoiding misleading claims or omitted information that could deceive users.
Data Collection and Use: Any collection of personal data must be transparent, lawful, and secure. Advertisers must have a proper privacy policy in place.
Manipulative or Abusive Tactics: Practices such as “cloaking” (showing different content to users and Google), phishing, or promoting false information are strictly prohibited. - Restricted Content
Certain types of content are allowed under specific conditions but are subject to additional restrictions and requirements:
Adult Content: Ads for adult-oriented content are restricted and only allowed in specific circumstances.
Alcohol: Advertising alcoholic beverages has restrictions that vary by country, including age targeting and regional laws.
Gambling and Games: Promoting gambling-related content is subject to legal restrictions and requires Google’s certification.
Healthcare and Medicines: Pharmaceutical products and health services are regulated, requiring adherence to local laws and policies.
Financial Services: Financial products and services, including loans, banking, and investments, must comply with disclosure and consumer protection standards.
- Editorial and Technical Quality
Clarity and Accuracy: Ads and websites must be clear, well-constructed, and error-free, ensuring users have a positive experience.
Technical Performance: Websites linked from ads must function adequately, load quickly, and be easily navigable.
Ad Format: Ads must comply with Google’s format requirements, including correctly using text, images, and video content. - Trademark Policies
Use of Trademarks: Google has specific policies regarding trademarked terms in ad content, ensuring respect for intellectual property rights.
Enforcement and Compliance
Google actively enforces its Ads policies through automated systems and manual reviews. Advertisers found in violation of these rules may see their ads disapproved, and repeated violations can lead to account suspension. Advertisers must familiarize themselves with and adhere to Google Ads policies to avoid disruptions in their advertising campaigns.
Keeping Updated
Google periodically updates its advertising policies in response to changes in laws, market conditions, and user feedback. Advertisers should regularly review the Google Ads policies to ensure ongoing compliance.
In conclusion, Google Ads is a pivotal component of digital marketing strategies, offering unmatched visibility, targeted advertising, and measurable results. Its comprehensive framework, encompassing various ad formats, bidding strategies, and strict adherence to quality and policy guidelines, ensures that advertisers can reach their desired audience efficiently and effectively. The platform’s emphasis on relevance and user experience aligns with the broader goals of digital marketing to connect with customers in meaningful and impactful ways.
Navigating the complexities of Google Ads, from understanding Ad Rank and Quality Score to complying with Google’s extensive rules, requires technical knowledge and strategic insight. This is where Digital Chandu Solution comes into play, offering top-tier digital marketing training and services. With a focus on equipping professionals and businesses with the skills and strategies needed to excel in digital marketing, Digital Chandu Solution stands out for its comprehensive training modules that cover all aspects of Google Ads and beyond. Their services are designed to help clients leverage digital marketing tools effectively, ensuring they meet and exceed their online marketing goals.
Whether new to digital marketing or looking to enhance your existing skills, Digital Chandu Solution provides the expertise and support needed to navigate the digital landscape successfully. With a commitment to excellence and a deep understanding of digital marketing dynamics, Digital Chandu Solution is your partner in unlocking the full potential of digital marketing strategies, including mastering Google Ads to achieve outstanding results.

